Use of Virtual Reality in Safety and Fire-fighting training: An emerging trend
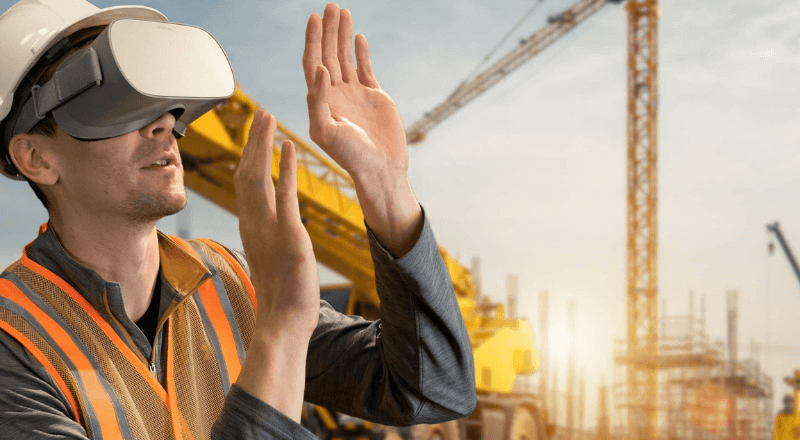
Virtual Reality technology is raising the bar in firefighter and safety training while helping save lives and conserve valuable resources. The use of VR technology allows training for incidents that cannot easily be replicated, are dangerous or may be very costly to recreate while eliminating the hazards involved in live training.
What is Virtual Reality (VR) and how does it differ from Augmented reality (AR)
AR is used on a smart device to project a layer of educational text and lesson-appropriate content on top of a user’s actual surroundings, providing users with interactive and meaningful learning experiences. However, VR creates an entirely digital environment, a 360-degree, immersive user experience that feels real. In a VR setting, users can interact with what they see as if they were there.
The combination of both technologies is known as mixed reality can improve user experience. For example, in a March 2019 report, EdTech, a global research organization for technology in education cites a study showing that students in a mixed reality biology classroom received higher scores than other students. And AR and VR can help with memory retention and recall, as well—EdTech reports on a recent study that shows an increase in retention of almost 9 percent for students who learned in an immersive environment such as VR.
Types of VR/AR training include
- Desk-based VR, using a computer monitor to display a 3D virtual world on a desktop screen
- Immersive VR that relies on specific hardware
- 3D, game-based VR that uses computer-based, video game-like training scenes via a combination of visual, interactive networks, and multi-user operating technologies
- Building Information Modelling (BIM)-enabled VR allows users to access BIM data to simulate construction, processes, and operations
Benefits of VR in Safety training
- Safe training environment with 360-degree views.
- The immersive nature of VR and AR is ideal for engaging the behavioural skills learning system. Users learn by doing, receive feedback and engage in repetitions of the skills they are learning. This process promotes the formation of habits.
- Immersive Learning places learners in realistic work environments without real-life dangers so that they can experience and apply to learn. This prepares them for health and safety challenges in the most comprehensive and lasting way.
- Portable with short setup time and reduced training costs.
- Deployable in the standard classroom at any training academy.
- Suitable for high-risk situations that cannot be trained live.
- Less wear and tear on personal protective equipment (PPE) and response equipment during fire-fighting training.
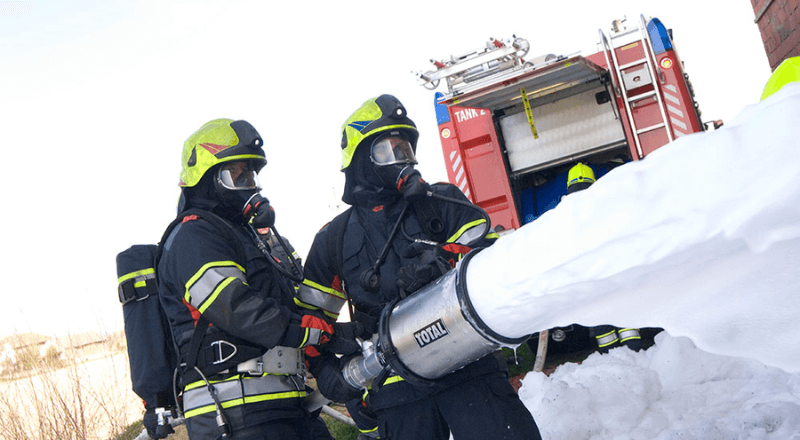
VR applications in Safety and Fire fighting
VR in safety training find application in many specialized areas such as
- Hazard recognition
- Fall protection
- Emergencies
- Safety protocol
- Lockout / Tagout
- Fire-fighting Nozzle tactics
- Ventilation techniques
- Fire Simulation
But certain conditions need to be taken care of while planning a VR training such as
Ensure Ample Physical Space: To reap the benefits of virtual reality in training, participants need to use VR equipment safely. VR users often spin around or stride blindly, ignoring their physical surroundings. A misstep could lead to injury. Educators should ensure their classrooms’ physical environments are spacious and safe for VR explorers.
Supervise and Moderate VR Use during training: Research into the psychological impact of VR on users suggests that VR should be used moderately and under close supervision. The findings of the research as reported in a recent CNN.com article recounts those children who overused VR had false memories of having physically visited a place they never visited. Limiting VR education sessions to a couple of minutes as part of a longer lesson plan can address this issue.
Know When to Use VR in the Classroom: VR can offer new insights and refreshing perspectives to participants, but VR can’t replace human interaction. Learning is fundamentally a social experience, so VR is best used as a supplemental learning tool.
Companies Using Virtual Reality for Employee Training
The fast-growing field of virtual reality is an increasingly common part of worker training, from offices to coal mines and athletic fields. Now, employers also are tapping VR to help recruit, train, and retain employees with VR simulations. By giving recruits and old hands immersive yet novel experiences that seem more like play than work, VR can inject enthusiasm and engagement where they may be lacking, helping employees see their jobs in a more positive light. Employee training is one of the areas that is benefiting the most from the immersive revolution.
BP uses virtual reality to train its employees in start-up and emergency exit procedures at its oil refinery in Hull, England. Employees were able to learn from mistakes in the virtual world and thus reduce the probability of making the same error in the real world – an error that could ultimately cost someone’s life.
ExxonMobil is using VR for safety training. Users can put on a helmet and headphones, grab a controller, and plug into the virtual world, engaging multiple senses. They can turn their heads, walk around and watch the VR world react. Immersive simulations can transport VR users onto the loading dock of a liquefied natural gas (LNG) tanker, where they spend a day on the job assessing and reacting to different scenarios, from the mundane to the complex. The experiences allow employees to hone their instincts, catch their mistakes, and make instant decisions so that they’re better equipped to work smarter and safer.
Conclusion:
When compared to a traditional training program, VR is an engaging technology that learners are likely to remember. VR training helps to capture and hold learners’ attention, leading to higher knowledge retention rates. However, it comes with a few drawbacks as well.
VR solutions can have higher costs than other solutions, which can also make scalability difficult. But the good news is that as VR becomes more popular, development costs and headset prices are going to come down considerably.
Some people can experience physical side effects when using VR. Common symptoms include headaches, nausea, and eyestrain. Steps must be taken to ensure that the content is carefully designed to avoid fatigue.
Many prominent players in the market provide VR infrastructure and training solutions and constantly improve their offerings such as STRIVR and FLAIM. Virtual Reality (VR) technology is changing the way we do business. In these past years, VR has faced a resurgence unlike ever before, especially when it comes to the development of VR professional training. Organizations shall consider VR & AR assisted training to help employees gain more knowledge, improve their skills, and for providing higher safety standards.